double fertilization in angiosperms results in:|Double Fertilization : Bacolod double fertilization, in flowering plant reproduction, the fusion of the egg and sperm and the simultaneous fusion of a second sperm and two polar nuclei that ultimately results in the formation of the endosperm (the food-storage tissue) of the seed. Rotten Tomatoes, home of the Tomatometer, is the most trusted measurement of quality for Movies & TV. The definitive site for Reviews, Trailers, Showtimes, and Tickets
double fertilization in angiosperms results in:,double fertilization, in flowering plant reproduction, the fusion of the egg and sperm and the simultaneous fusion of a second sperm and two polar nuclei that ultimately results in the formation of the endosperm (the food-storage tissue) of the seed.This is called double fertilization because the true fertilization (fusion of a sperm .
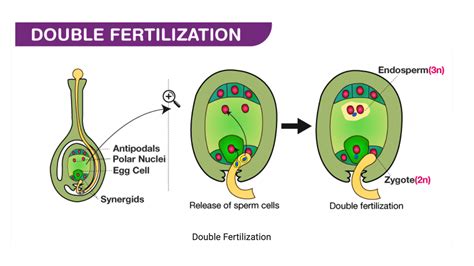
Pollination helps the pollen grains to reach stigma via style. The two sperm cells enter the ovule-synergid cell. This proceeds to . Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Double fertilization: In angiosperms, one sperm fertilizes the egg to form the 2n zygote, while the other sperm fuses with two polar nuclei .Double fertilization or Double fertilisation (see spelling differences) is a complex fertilization mechanism of flowering plants (angiosperms). This process involves the joining of a female gametophyte (megagametophyte, also called the embryo sac) with two male gametes (sperm). It begins when a pollen grain adheres to the stigma of the carpel, the female reproductive structure of a flower. The pollen .
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Double fertilization: In angiosperms, one sperm fertilizes the egg to form the 2n zygote, while the other sperm fuses with two polar nuclei .
In angiosperms, sexual reproduction results in two structures, namely, zygote and endosperm, hence the name double fertilization. Schematic representation .Double Fertilization In angiosperms, sexual reproduction results in two structures, namely, zygote and endosperm, hence the name double fertilization. Schematic representation .Abstract. In angiosperm plants the interaction between male and female gametophytes, the pollen tube and the embryo sac respectively, results in double fertilization. The pollen .In angiosperms, one sperm fertilizes the egg to form the 2 n zygote, and the other sperm fertilizes the central cell to form the 3 n endosperm. This is called a double fertilization. After fertilization, the zygote divides to .
The launch of seed development in flowering plants (angiosperms) is initiated by the process of double fertilization: two male gametes (sperm cells) fuse with . The fertilized ovule forms the seed, whereas the tissues of the ovary become the fruit, usually enveloping the seed. Figure 40.5.3.1 40.5.3. 1: Double fertilization: In angiosperms, one sperm fertilizes the egg to form the 2n zygote, while the other sperm fuses with two polar nuclei to form the 3n endosperm. This is called a double fertilization.In angiosperms, one sperm fertilizes the egg to form the 2 n zygote, and the other sperm fertilizes the central cell to form the 3 n endosperm. This is called a double fertilization. After fertilization, the zygote divides to .

Sexual reproduction in plants results in: (Select all that apply.) a. increased genetic diversity. b. offspring that are genetically different from each other. c. offspring that are genetically different from the parent(s). . Double fertilization in angiosperms results in a: a. diploid embryo and a haploid endosperm. b. diploid embryo and a .double fertilization in angiosperms results in: Double Fertilization Sexual reproduction in plants results in: (Select all that apply.) a. increased genetic diversity. b. offspring that are genetically different from each other. c. offspring that are genetically different from the parent(s). . Double fertilization in angiosperms results in a: a. diploid embryo and a haploid endosperm. b. diploid embryo and a .Fertilization in Angiosperms S.D. Russell 14.1 Introduction Inthe current review, focus is directedtothe mostrecentfindings, withanattemptto integrate critical information that is useful in understanding the current biological context of double fertilization research in angiosperms. An attempt has been made Figure 26.3C. 1 26.3 C. 1: Life cycle of angiosperms: The life cycle of an angiosperm is shown. Anthers and carpels are structures that shelter the actual gametophytes: the pollen grain and embryo sac. Double fertilization is a process unique to angiosperms. The ovule, sheltered within the ovary of the carpel, contains the . Abstract. Double fertilization in angiosperms results in the formation of a second zygote, the fertilized endosperm. Unlike its embryo sibling, the endosperm is a transient structure that eventually undergoes developmentally controlled programmed cell death (PCD) at specific time points of seed development or germination. Double fertilization in angiosperms was first discovered by Guignard , Nawaschin . One sperm cell fuses with the egg cell to form an embryo while the other fuses with the central cell forming the endosperm, which provides nourishment to the developing embryo (Shin et al. 2020). Thus, in angiosperms, nutrient supply becomes dependent . This animation explains the double fertilization process in flowering plants (Angiosperms). It was created as a co-production between the School of Bioscienc. The launch of seed development in flowering plants (angiosperms) is initiated by the process of double fertilization: two male gametes (sperm cells) fuse with two female gametes (egg and central cell) to form the precursor cells of the two major seed components, the embryo and endosperm, respectively. The immobile sperm cells are .

The process of fertilization in plants is a remarkable and intricate mechanism that ensures the continuation of their species. In angiosperms, the most diverse and widespread group of plants on Earth, a fascinating phenomenon known as double fertilization occurs. This distinctive reproductive strategy sets angiosperms apart and plays a crucial role in their .double fertilization in angiosperms results in: Double fertilization is a fertilization mechanism in flowering plants or angiosperms. The process involves the fusion of one female gamete or egg cell (megagametophyte, or the embryo sac) with two . The launch of seed development in flowering plants (angiosperms) is initiated by the process of double fertilization: two male gametes (sperm cells) fuse with two female gametes (egg and central cell) to form the precursor cells of the two major seed components, the embryo and endosperm, respectively. The immobile sperm cells are .What is the result of double fertilization in an angiosperm? a. a diploid zygote and haploid polar nucleus. . Features of Angiosperms: Angiosperms are a group of plants that are characterized by the presence of flowers. Flowers are essential in ensuring that the seeds are formed. There are two main types of flowers which are complete and .
Double fertilization is a major characteristic of flowering plants (angiosperms). This complex process involves intensive cross-talk between the male gametophyte (pollen and pollen tube, respectively) with the female tissues of the pistil (e.g., stigma, style, and ovule) and the female gametophyte (embryo sac), respectively (Dresselhaus .Angiosperms undergo a type of double fertilization that produces an embryo and an endosperm, a nutrient store. The embryo and endosperm are packed into a seed coat, forming a seed. As the ovules become seeds, the ovary typically develops into fruit that helps protect and distribute the seeds. Suggested Reading.
Botany. Biology 102: Chapter 29 (From the homework) Select the correct statement describing the life cycle of angiosperms. -Double fertilization in the life cycle of seed plants results in the production of a diploid zygote and a triploid endosperm nucleus. -In angiosperm life cycles, the female gametophyte is the ovule.Things to Remember. Double fertilization is the process of fusion of two male gametes with one female gametophyte. Angiosperms (flowering plants) reproduce through the process of double fertilization. The process involves .
Define double fertilization. In angiosperms, pollination is defined as the placement or transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or another flower. In gymnosperms, pollination involves pollen transfer from the male cone to the female cone. Upon transfer, the pollen germinates to form the pollen tube and the sperm for .
double fertilization in angiosperms results in:|Double Fertilization
PH0 · The beginning of a seed: regulatory mechanisms of double
PH1 · Process & Significance Of Double Fertilization
PH2 · Fertilization in Angiosperm Plants
PH3 · Double fertilization
PH4 · Double Fertilization in Plants
PH5 · Double Fertilization in Angiosperms
PH6 · Double Fertilization
PH7 · 40.5.3: Double Fertilization in Plants